Part D Star Ratings Adherence Measures: Enabling Strategic and Focused Support for High-risk Beneficiaries Through the Reporting and Intervention for Stars Excellence (RISE) Program
Authors: Wenxuan Cai, PharmD, PhD; Amanda Lee, PharmD; Caitlin Albrecht, PharmD; Maria Basak, CPhT; Casey Herlache; Capriana Hadel, MBA
Executive Summary
Adherence to key medication classes is a critical metric for evaluating health plan quality and continuous improvement of health care services. Given the impacts of medication adherence on health care outcomes, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Star Rating System has prioritized specific adherence measures over other clinical measures in the calculation of Part D Star Ratings. Although patient outreach remains a hallmark of a robust Star Rating support offering, a data-driven program that focuses high-touch, member-centric and consultative support on a select and continually refined subset of a health plan’s beneficiary population will result in more meaningful and positive impacts on CMS Star Rating performance.
The Reporting and Intervention for Stars Excellence (RISE) Program was developed to facilitate member identification, engagement and clinical support, with qualification occurring via a continuous feedback loop for near real-time refinement. The program also leverages analytics with intermediate and long-term outcome metrics to track progress toward specified Star Ratings goals.
The RISE Program was deployed for a regional Medicare health plan covering over 25,000 beneficiaries. Through strategic member identification, personalized support and real-time performance reporting, the RISE Program enabled significant improvements in adherence to antihypertensive, antidiabetic and cholesterol-lowering medications. Medication adherence was measured by proportion of days covered (PDC) in alignment with CMS Star Ratings technical specifications. This paper highlights the RISE Program methodology, key findings and broader implications for health care quality improvement. Additionally, operational and technical challenges and opportunities are discussed with recommendations for future development.
Introduction
Nonadherence to medications remains a significant barrier to achieving optimal health outcomes, particularly among individuals with chronic conditions.1, 2, 3 Among Medicare beneficiaries, poor adherence is associated with increased hospitalizations and higher health care costs, leading to diminished quality of life and increased mortality.4,5 The CMS Medicare Advantage and Part D Star Ratings System provides a framework for assessing the quality of participating health plans and is used to guide performance-improvement initiatives. Within this system, medication adherence measures are key contributors to a plan’s Overall Star Rating. The Part D Star Ratings measures specifically target adherence to antihypertensive medications (renin-angiotensin system antagonists), antidiabetic medications (blood glucose-lowering agents excluding insulins) and cholesterol-lowering medications (HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, commonly known as statins). A beneficiary is considered adherent if they achieve a proportion of days covered (PDC) of at least 80% for the prescribed medication.
To date, few clinical programs have successfully demonstrated meaningful improvements in adherence-related Part D Star Ratings measures. Traditional interventions often fall short due to ineffective member identification strategies, limited multi-source data integration and a lack of scalable reporting capabilities. These gaps can result in poor prioritization, fragmented workflows and operational inefficiencies. In response to these challenges, our organization developed a comprehensive, software-driven solution designed to enable proactive member identification and prioritization, multimodal engagement, continuous monitoring and real-time performance reporting. Insights from the implementation of the RISE Program, detailing its design, effectiveness and real-world impact, are included in this white paper.
Primary Objectives of the RISE Program
Improve Medication Adherence Part D Star Measures
Increase adherence rates among beneficiaries prescribed antihypertensive, antidiabetic and cholesterol-lowering therapies. These are referred to as the hypertension (HTN), diabetes (DM) and cholesterol (HLD) measures, respectively, in this manuscript.
Enable High-touch Beneficiary Support
Engage beneficiaries, prescribers and pharmacies through multiple communication channels. Deliver scalable, cost-effective and personalized clinical support to improve adherence outcomes and beneficiary experience.
Generate Actionable Insights
Leverage automation and data analytics to support ongoing monitoring and continuous refinement of engagement strategies by clinical or care coordination staff.
Study Design and Methodology
Population
The study included over 25,000 Medicare beneficiaries enrolled in a regional health plan.
Intervention and Control
The RISE Program was implemented in 2023. Historical adherence data immediately prior to program implementation (2022) from the same health plan was used as a control to evaluate the impacts of the program and associated services.
Primary Outcomes
One of the primary outcomes is the change in the proportion of qualified beneficiaries achieving a PDC of at least 80% for each of the Part D adherence measures (HTN, DM and HLD).
Another primary outcome evaluated is the correlation between RISE Program intervention and medication adherence. This is evaluated by measuring the proportion of beneficiaries who received the RISE Program intervention and achieved a PDC of at least 80%, compared to those who did not receive intervention.
Secondary Outcome
The secondary outcome is the patient experience and perceived usefulness of clinical support through completion of a telephonic customer satisfaction survey (CSAT).
Statistical Analysis
To evaluate changes in Part D Star Ratings adherence and measure performance before and after implementation of the RISE Program, chi-square tests were used to assess differences across groups. Statistical significance was defined as a two-tailed p-value less than 0.05. For multiple group comparisons, Bonferroni-adjusted tests were performed to account for the risk of type I error.* To examine the association between RISE Program intervention and medication adherence, logistic regression analysis was conducted with multivariable adjustment for age, gender, primary language and prior-year adherence status. Adjusted odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were derived from the regression models. All statistical analyses were performed using RStudio (version 4.3.1).
*A type 1 error is an error of detecting statistically significant difference when such difference does not exist.
Software Platform and Overview
The in-house software platform underpinning the RISE Program integrates data from multiple sources, including eligibility files, pharmacy and medical claims information. Advanced qualification algorithms are used to identify beneficiaries who are nonadherent or at risk for medication nonadherence. Those who meet the predefined criteria are automatically enrolled in the RISE Program. The platform also serves as a centralized solution, enabling the delivery of personalized and data-driven interventions at scale.
The key features include:
Strategic Beneficiary Identification and Prioritization
The platform leverages multiple data sources, advanced analytics and predefined qualification criteria to analyze pharmacy claims data and identify beneficiaries who are nonadherent to prescribed medications or at risk for nonadherence. Eligible beneficiaries are automatically enrolled in the RISE Program. The system continuously evaluates updated claims data to adjust outreach queues and facilitate dynamic task prioritization. Users can further refine intervention strategies based on program type, prescription fill patterns and the beneficiaries’ nonadherence risk level.
Multichannel Communication
By integrating beneficiary demographic information, pharmacy and prescriber details, and claims data, the platform enables personalized multichannel communication. Outreach efforts can be directed toward beneficiaries or their authorized representatives, pharmacies and/or prescribers to deliver targeted clinical support and improve adherence outcomes.
Clinical Documentation
The platform supports efficient clinical documentation by capturing detailed intervention notes, communication history and outcomes tracking. This functionality ensures transparency, continuity of care and compliance with internal protocols and regulatory standards.
On-demand Analytics and Reporting
The analytics dashboards provide near real-time insights into program performance, member engagement and adherence trends. These reporting tools enable stakeholders to monitor progress, identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to optimize program impact.
Key Findings
In 2023, the RISE Program was implemented for a regional Medicare health plan covering over 25,000 beneficiaries. Program impact was evaluated by comparing medication adherence Part D Star Ratings measures before implementation (2022) and after implementation (2023 and 2024). Although the plan transitioned from a Managed Medical Plan (MMP) to a Dual Eligible Special Needs Plan (D-SNP) during this time, approximately 71% of beneficiaries in 2022 remained enrolled in 2023, and the overall benefits offered remained consistent throughout the transition.
As shown in Table 1, the population characteristics remained stable across the evaluation period (2022–2024). Notably, there was a slight year-over-year increase in the proportion of enrollees whose primary language was Spanish or another non-English language. Prior research has identified language barriers or ethnic minority status as significant contributors to medication nonadherence6,7, suggesting the post-implementation population faced additional challenges in adherence and may have required more targeted support.
Table 1: Demographic Characteristics of the Study Population
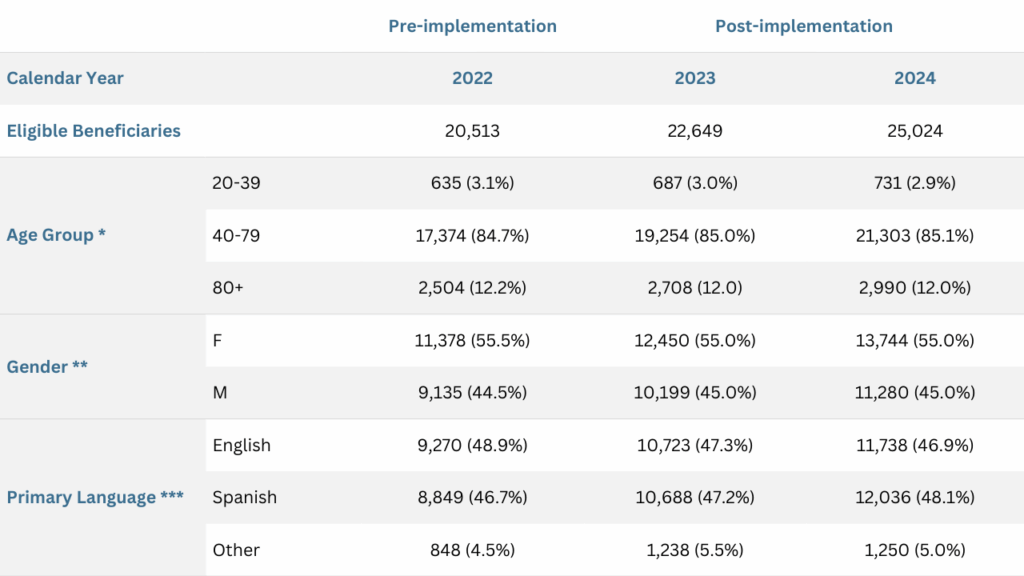
*, **. There were no statistically significant differences observed in the age group or gender distribution among beneficiaries enrolled in the plan from 2022 to 2024.
***. A small but statistically significant increase in the proportion of enrollees speaking Spanish or another non-English language was observed in 2023 and 2024 compared to 2022.
Improved Medication Adherence Part D Star Ratings Measures After Implementation of RISE Program
Following the implementation of the RISE Program, there was an increase in the proportion of beneficiaries achieving a PDC of 80% or above for their prescribed medication therapy over the evaluation period (Figure 1). Compared to pre-implementation, adherence measures for HTN, DM and HLD improved by 4.1%, 4.0% and 5.3%, respectively, after implementation. These changes were statistically significant (Table 2).
Figure 1: Comparison of the HTN, DM and HLD Measures Before and After Implementation of the RISE Program (2022-2024)
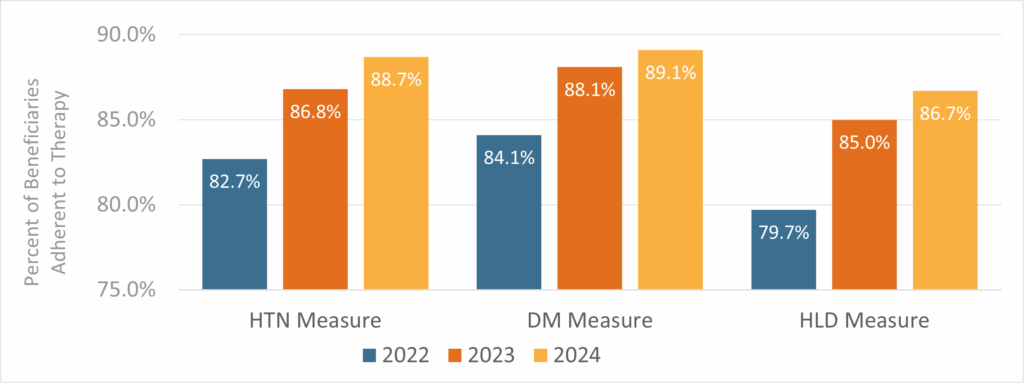
The CMS criteria for synthesizing each measure were applied in the analysis. Beneficiaries were considered adherent if their medication PDC was at least 80%. Adherence rates were calculated at the end of each year. The 2022 data represent pre-implementation rates, prior to the availability of the RISE Program, while the 2023 and 2024 data reflect results after implementation.
Table 2: Detailed HTN, DM and HLD Measures Before and After Implementation of the RISE Program
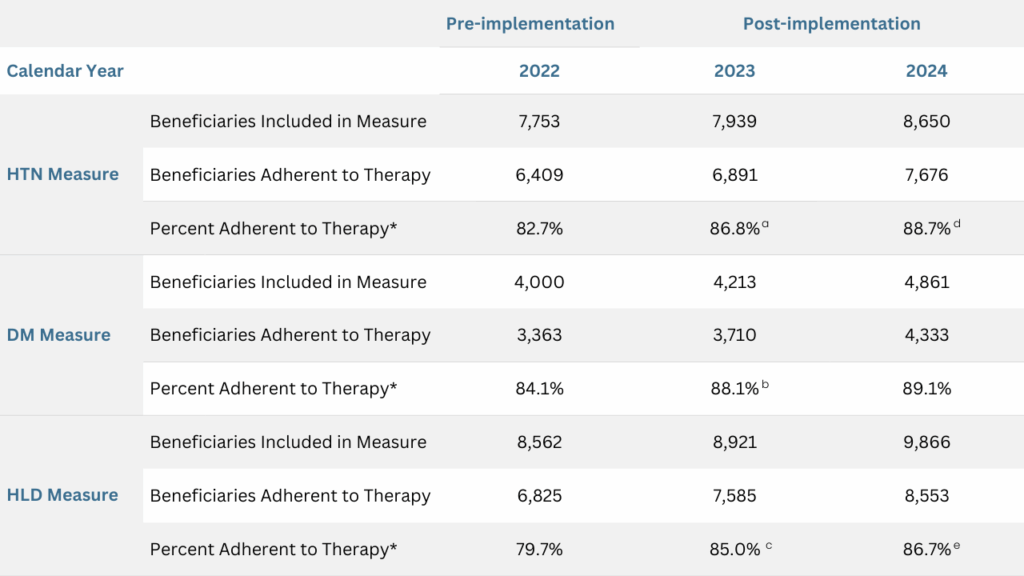
The CMS criteria for synthesizing each measure were applied to the analysis. Beneficiaries were considered adherent if their medication PDC was at least 80%. The adherence rates were calculated at the end of the year.
*Statistically significant differences were observed among groups with two-tailed p-values <0.00001.
a, b, c. Statistically significant differences observed compared to 2022, with Bonferroni-adjusted two-tailed p-values <0.0001.
d, e. Statistically significant differences observed compared to 2023, with Bonferroni-adjusted two-tailed p-values <0.001 and <0.05, respectively.
The positive trends in adherence Part D Star Ratings measures continued into 2024, although with smaller effect sizes compared to 2023 (Figure 1). This was anticipated, as the remaining nonadherent beneficiaries may have faced greater challenges in the management of complex medical conditions and medications. Nonetheless, the improvements in HTN and HLD measures from 2023 to 2024 were statistically significant.
This data demonstrates substantial improvements in medication adherence Part D Star Ratings measures following the implementation of the RISE Program in a large regional health plan with a diverse group of beneficiaries.
Beneficiaries Receiving RISE Program Clinical Support Were More Likely to Adhere to Prescribed Therapy
To evaluate the correlation between the clinical support via the RISE Program and medication adherence, a detailed analysis was conducted to compare adherence rates among beneficiaries who received RISE Program clinical support versus those who did not. In the 2023 program year, a total of 2,477 beneficiaries in the HTN measure, 1,051 in the DM measure and 3,044 in the HLD measure, were automatically enrolled in the RISE Program (Table 3). Enrolled beneficiaries had lower overall adherence rates compared to the broader population (57.8% vs 86.8%, 53.1% vs 88.1%, and 57.2% vs 85.0%, for HTN, DM and HLD measures, respectively) (Tables 2 and 3). These differences support the validity of the RISE qualification logic.
Among those enrolled in the RISE Program, beneficiaries who received clinical consultation and support showed higher adherence rates compared to those who did not receive interventional support (Figure 2). Logistic regression analysis was performed with multivariable adjustments for age, gender, language and adherence status in the previous year. After controlling for these factors, beneficiaries who received the RISE intervention were 33%, 15%, and 15% more likely to adhere to their prescribed therapy for HTN, DM and HLD, respectively (Table 3). The result was statistically significant for the HTN measure (adjusted OR: 1.33, 95% CI: 1.12–1.57). The adjusted ORs for the DM and HLD measures were 1.15 (95% CI: 0.89 – 1.48) and 1.15 (95% CI: 0.99 – 1.33), which did not reach statistical significance, likely due to limited statistical power.
Figure 2: Beneficiaries Who Received Clinical Support Via the RISE Program Had a Higher Adherence Rate Compared to Those Who Did Not
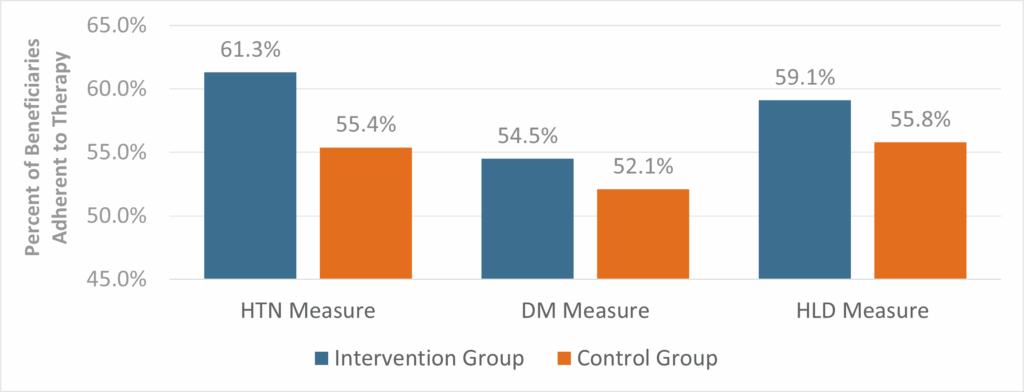
CMS criteria for synthesizing each measure were applied in the analysis. Beneficiaries were considered adherent if their medication PDC was at least 80%. Adherence rates were calculated at the end of program year 2023. The intervention group includes beneficiaries who were qualified into the RISE Program and received clinical support. The control group includes beneficiaries who were qualified into the RISE Program but did not receive clinical support.
Table 3: Successful RISE Program Clinical Support is Positively Associated with Adherence to Prescribed Medication Therapy
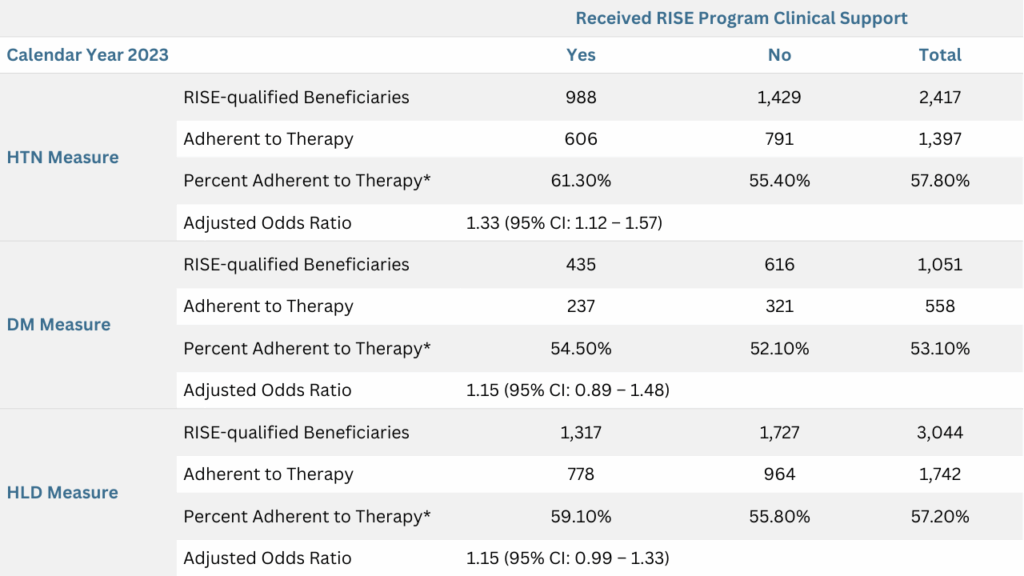
*The CMS criteria for synthesizing each measure were applied in the analysis. Beneficiaries were considered adherent if their medication PDC was at least 80%. Adherence rates were calculated at the end of each year. Odds ratios were derived from logistic regression analysis, adjusting for age, gender, primary language spoken and prior-year PDC.
Collectively, the analyses of the beneficiaries enrolled in the RISE Program demonstrated positive association between RISE Program clinical support and improved adherence to prescribed medication therapy.
Clinical Services Delivered Through the RISE Program Were Positively Received by Beneficiaries
Clinical services delivered through the RISE Program were well-received by beneficiaries, reinforcing the value of personalized and high-touch support in improving medication adherence. Feedback collected from beneficiary interactions indicated a high level of satisfaction with the clinical consultations, with 90% of post-call survey respondents rating their satisfaction as 5 out of 5 (on a scale of 1 to 5, with 5 being extremely satisfied) (Figure 3). The beneficiary post-call satisfaction score (CSAT) was 97% (Figure 3). Many beneficiaries expressed appreciation for the clarity, empathy and support provided. These services helped address individual barriers to adherence, such as medication confusion, side effects and access issues. By fostering trust and engagement, the RISE Program not only improved clinical outcomes but also enhanced the overall beneficiary experience. This positive reception highlights the importance of incorporating human-centered approaches into technology-driven health care interventions.
Figure 3: Beneficiary Satisfaction Rating of the Clinical Services Delivered Through the RISE Program
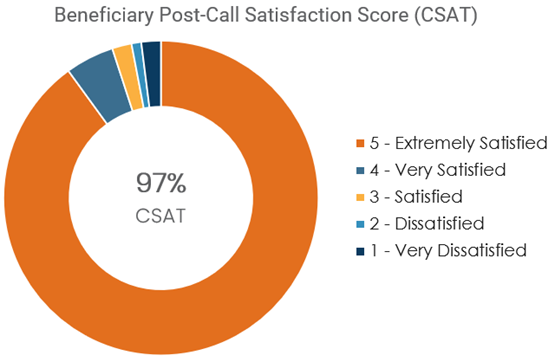
Beneficiaries completing the post-call survey rated their experience on a scale of 1 to 5, with 5 being extremely satisfied.
Discussion
The implementation of the RISE Program as administered by Navitus demonstrated measurable improvements in medication adherence across key CMS Part D Star Ratings measures for antihypertension, antidiabetic and cholesterol-lowering therapies. Through a combination of data-driven identification, tailored outreach, multi-channel communication and advanced reporting, the implementation effectively addressed common challenges that hinder the success of traditional adherence improvement programs. Beneficiaries who received clinical support services were more likely to achieve adherence after controlling for common confounders including demographic and historical adherence factors. The intervention had the greatest impact on the HTN measure, likely due to the ease of assessing treatment effectiveness and the well-perceived favorable outcomes of preventing the dangerous consequences of uncontrolled high blood pressure, such as stroke. Additionally, positive association was observed for the DM and HLD measures, despite not reaching statistical significance, probably due to limited statistical power. The consistent direction of effect, in combination with overall improvement in the key Part D Star Ratings measures at the population level, strongly support the value of this data-driven clinical intervention program.
Operationally, the platform demonstrated scalability and efficiency by automating beneficiary enrollment, prioritization and reporting, which reduced administrative burden while improving operational workflow and intervention success. The high satisfaction scores further validate the importance of integrating people-centered services within technology-driven programs. Notably, the RISE Program achieved these outcomes within a large regional health plan serving a highly diverse group of beneficiaries, supporting its potential for broader adoption across other health plans.
Some limitations of the study include its observational design and the challenge of assessing downstream outcomes, such as clinical endpoints and overall health care costs. Additionally, the implementation and evaluation focused on ambulatory populations, leaving the impact on facility-residing beneficiaries unclear. Future research should explore these dimensions, including modifiable contributors of nonadherence, to better inform adherence improvement strategies.
The ongoing development of the platform focuses on supporting additional CMS Part D Star Ratings measures, such as Statin Use in Persons with Diabetes (SUPD), Polypharmacy: Use of Multiple Anticholinergic Medications in Older Adults (Poly-ACH) and Concurrent Use of Opioids and Benzodiazepines (COB). This could not only improve overall quality ratings but also enhance beneficiary experience by enabling clinicians to address multiple clinical issues in a single encounter. Enhanced communication features, such as two-way texting, may also improve engagement with hard-to-reach beneficiaries. Expanding the RISE Program to include facility-residing populations will provide further insights into its broader applicability.
Conclusions
The RISE Program is an integrated data-driven clinical engagement program that represents a scalable and effective approach to improving medication adherence across key CMS Part D Star Ratings measures. By addressing long-standing challenges in traditional adherence programs through strategic beneficiary identification, streamlined operation and personalized engagement, the program demonstrated both clinical and operational successes. These findings not only validate the immediate value of the program but also highlight its potential for broader application across diverse health plan populations. As the program and platform continue to evolve with expanding capabilities, they stand to play a critical role in advancing quality of care, improving health outcomes and delivering long-term value for health plans and Medicare beneficiaries.
Disclosure: This research was conducted by Navitus Health Solutions, Madison, WI without external funding. All authors are employees of Navitus Health Solutions.
References
1. Cutler RL, Fernandez-Llimos F, Frommer M, Benrimoj C, Garcia-Cardenas V. Economic impact of medication non-adherence by disease groups: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2018;8(1):e016982. Published 2018 Jan 21. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016982
2. Ho PM, Rumsfeld JS, Masoudi FA, et al. Effect of medication nonadherence on hospitalization and mortality among patients with diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(17):1836-1841. doi:10.1001/archinte.166.17.1836
3. Lee EKP, Poon P, Yip BHK, et al. Global Burden, Regional Differences, Trends, and Health Consequences of Medication Nonadherence for Hypertension During 2010 to 2020: A Meta-Analysis Involving 27 Million Patients. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022;11(17):e026582. doi:10.1161/JAHA.122.026582
4. Zhang Y, Flory JH, Bao Y. Chronic Medication Nonadherence and Potentially Preventable Healthcare Utilization and Spending Among Medicare Patients. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(14):3645-3652. doi:10.1007/s11606-021-07334-y
5. Lloyd JT, Maresh S, Powers CA, Shrank WH, Alley DE. How Much Does Medication Nonadherence Cost the Medicare Fee-for-Service Program?. Med Care. 2019;57(3):218-224. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001067
6. Steve Tsang CC, Browning J, Todor L, et al. Factors associated with medication nonadherence among Medicare low-income subsidy beneficiaries with diabetes, hypertension, and/or heart failure. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2021;27(8):971-981. doi:10.18553/jmcp.2021.27.8.971
7. Patel D, Jalal Z, Guo P. Medicine Adherence and Associated Factors in Immigrants and Refugees: A Systematic Review. Int J Clin Pract. 2022;2022:1993066. Published 2022 Dec 28. doi:10.1155/2022/1993066
Stay Informed and Connected
Receive expert insights, healthcare tips, and important updates on pharmacy benefits, drug recalls, and more—straight to your inbox.
Navigating with a trusted partner
Now Available: 9th Annual Drug Trend Report
Our Drug Trend Report provides a clear view of the trends shaping pharmacy benefits today, along with strategies that are delivering real savings without compromising care.