An Automated Approach to Diagnosis Verification of GLP-1 RA for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM)
Authors: Trey Jones, PharmD; Agata Siwak, PharmD, MSBA; Marnie Wickizer, PharmD, AE-C, CDCES; Ryan Schmidt, PharmD; Robert Topp, RN, PhD
Abstract
This study examines the impact of implementing an automated point-of-sale diagnosis verification system for glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) compared to traditional utilization management approaches. Analysis of pharmacy claims data from 297,514 members showed that requiring diagnosis codes at point-of-sale effectively controlled both utilization and costs while maintaining appropriate access to medication. The intervention group saw a minimal increase in utilization (1.36% to 1.45%) compared to the control group (4.11% to 6.80%), with corresponding containment of per-member-per-month costs (PMPM) (15% vs 79% increase). Among claims initially rejected due to missing diagnosis codes, 78% were resolved within one day, suggesting this approach successfully balances cost control with timely access to medication. These findings indicate that automated diagnosis verification represents a promising alternative to traditional prior authorization for medications where diagnosis confirmation is the primary utilization management criterion.
Executive Summary
The growing utilization of GLP-1 RA medications represents both an opportunity and a challenge for healthcare payers and providers. The American Diabetes Association recognizes these medications as first-line therapies for T2DM. They are also among the costliest therapies for T2DM, with monthly drug costs ranging from $726 to $1,022 per patient. In addition, use of GLP-1 RA products indicated for T2DM for weight loss has increased, despite not being originally intended for that use. Many payers only cover these drugs for T2DM and desire to manage use accordingly. This white paper examines an innovative approach to diagnosis verification that automates utilization management at the point-of-sale, demonstrating significant improvements in both cost management and treatment access compared to traditional methods.
The Growing Challenge of GLP-1 RA Medication Management
Traditional management approaches, primarily centered around prior authorization, face significant operational challenges. Prior authorizations require substantial resources from providers, pharmacists and payers, while possibly delaying patient access to needed medications. As public awareness and demand for GLP-1 RAs continue to grow, particularly for off-label or non-covered use for weight loss, the volume of authorization requests strain existing resources.
A New Approach to Diagnosis Verification
To address these challenges, proof of a covered medical diagnosis at the point of sale is an alternative strategy for verifying acceptable use upon submission of the pharmacy claim. This method automates diagnosis verification via an innovative claim adjudication system design. Under this approach, pharmacies must submit International Classification of Diseases (ICD) diagnosis codes with claims for GLP-1 RA medications intended for T2DM.
This research examined this new approach, which was implemented on October 1, 2022, with a planned three-month transition period that ended on January 1, 2023. During the transition period, claims were paid for existing GLP-1 RA utilizers without diagnosis codes to ensure continuity of care while systems and processes were put in place. After the transition period, diagnosis codes were required for GLP-1 RA claims to pay.
Research Findings: Measuring Real-World Impact
To evaluate the effectiveness of this approach, researchers conducted a comprehensive study analyzing pharmacy claims data from 297,514 unique members. The study compared a group of 233,747 members enrolled in health plans that required diagnosis codes against a control group of 63,767 members enrolled in plans without such requirements. The demographics were similar between groups, with a mean age of 53 ± 10 years in the intervention group and 52 ± 11 years in the control group.
The results demonstrated clear benefits in both utilization management and cost containment. In the group requiring diagnosis codes (“intervention group”), the proportion of members utilizing GLP-1 RA medications showed minimal increase from 1.36% to 1.45% over 12 months. This contrasted sharply with the control group, which saw utilization climb from 4.11% to 6.80% over 12 months.
Cost implications were equally significant. The control group experienced a 79% increase in PMPM total cost, while the intervention group saw only a 15% increase. This differential represents substantial cost avoidance while maintaining appropriate access for patients with documented T2DM diagnoses who are prescribed these increasingly preferred therapies.
Table 1: Pre- and Post-Diagnosis Code GLP-1 RA Utilization Trend
|
Outcome |
Intervention Group |
Control Group |
|---|---|---|
|
Pre-diagnosis code GLP-1RA utilizers (%) |
2,928 (1.36%) |
2,294 (4.11%) |
|
Post-diagnosis code GLP-1RA utilizers (%) |
3.110 (1.45%) |
3,548 (6.80%) |
.
Figure 1: Change in GLP-1 RA Utilization
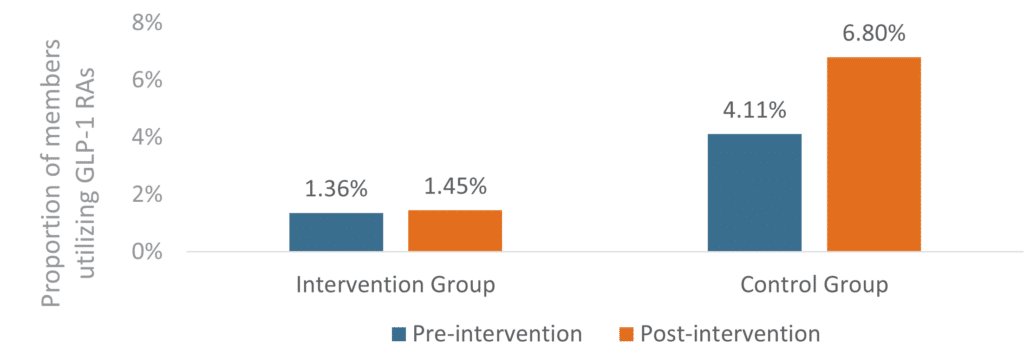
The proportion of overall members utilizing GLP-1 RA medications did not significantly increase in the intervention group (P = 0.016) but did significantly increase in the control group (P < 0.0001). The difference in differences was -2.6% favoring the intervention group.
Figure 2: Change in GLP-1 RA PMPM Total Cost
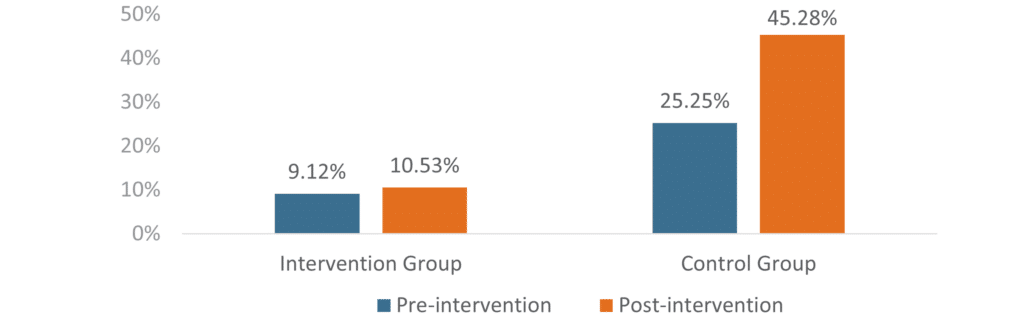
The control group had a greater percentage increase in PMPM total cost compared to the intervention group.
Impact on Treatment Access and Clinical Care
The study carefully examined the impact on patients’ access to medications. Among prescription claims initially rejected due to missing diagnosis codes, 45% were subsequently approved with proper documentation. For these approved claims, the process proved to be efficient: 78.3% were processed within one day, and 89.6% within four days of the initial rejection. The mean delay in dispensing was 2.4 days (± 8.9 days), in comparison to an often extended, multistep process that requires action to order, submit and approve a prior authorization.
These findings suggest that the automated verification system successfully balances two crucial objectives: controlling off-label or not-covered utilization while maintaining timely access for patients with a documented medical need. The rapid resolution of most rejected claims indicates that pharmacies quickly adapt to the new requirements and develop efficient processes for obtaining and submitting diagnosis verification.
Figure 3: Month-by-Month GLP-1 RA Utilization Trend
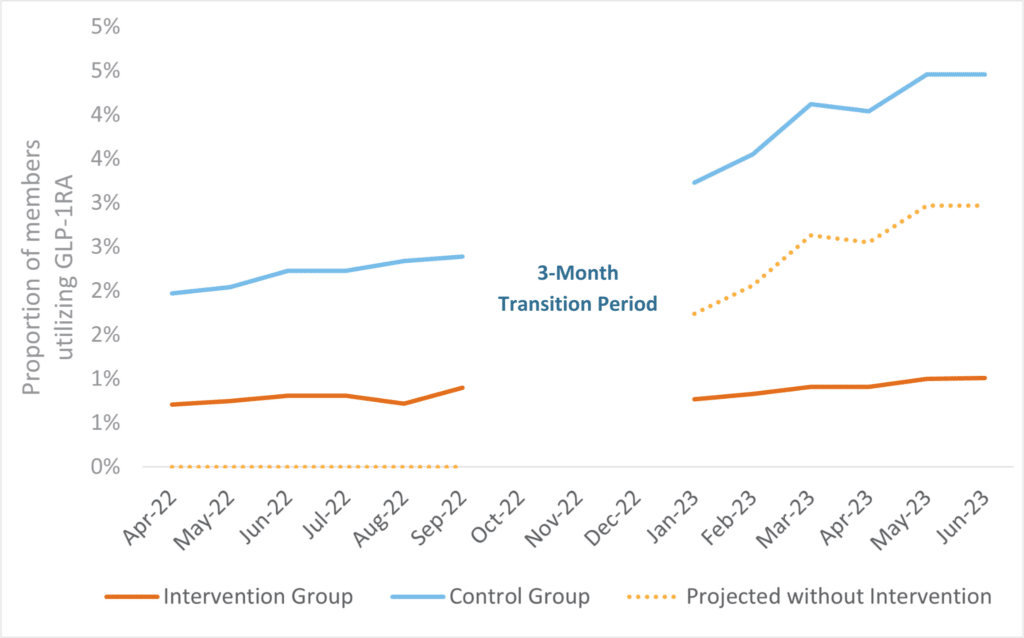
Projected data were calculated using a difference-in-differences approach assuming the intervention group changed at the same rate as the control group. No data were analyzed during the three-month transition period as claims were paid without diagnosis codes in both cohorts for existing GLP-1 RA utilizers.
Benefits Across the Healthcare Ecosystem
The impact of this automated diagnosis verification creates value for all stakeholders in the healthcare system. Health plans and employer plan sponsors benefit from significant cost containment through utilization management with potential reduced administrative costs, compared to a traditional method. The automated verification process requires minimal oversight while maintaining effective controls.
For pharmacies and healthcare providers, the streamlined workflow represents a significant improvement over the traditional utilization management methods, such as prior authorization. The requirements are clear for diagnosis code entry, and approval feedback is immediate, allowing for quick resolution of any issues. This approach integrates seamlessly with existing pharmacy systems, minimizing disruption to established workflows.
Perhaps most importantly, patients benefit from faster access to appropriately prescribed medications. Minimal delays in therapy and reduced administrative burden support better adherence to prescribed treatments while ensuring appropriate utilization.
Limitations and Considerations
While the research demonstrated clear benefits of automated diagnosis verification, several important limitations should be considered when evaluating this approach. The study design did not account for baseline differences between the intervention and control groups that may have affected GLP-1 RA utilization. Important variables that could impact outcomes include region-specific prescribing patterns, prevalence of diabetes, prevalence of obesity and socioeconomic status. A propensity-matching approach might have yielded more balanced study groups and increased the internal validity of the findings.
The relatively short duration of 12 months provides limited insight into the long-term effects of the diagnosis code requirement. For example, there may be a learning effect where pharmacies become more proficient at acquiring diagnosis verification over time, potentially improving efficiency beyond what was observed in this initial study period. Conversely, long-term challenges or limitations might only become apparent with extended observation.
An important consideration is that direct comparisons to prior authorization outcomes were not part of the study design. Future research comparing these approaches head-to-head could provide valuable insights into their relative effectiveness.
Future Applications and Conclusions
The successful implementation of automated diagnosis verification for GLP-1 RA demonstrates the potential for streamlined utilization management approaches in pharmacy benefit design. This strategy requires minimal technical infrastructure – primarily the capability to submit diagnosis codes and maintain documentation – yet delivers significant impact on both cost containment and treatment access.
The study results show clear benefits: the diagnosis code group experienced minimal increase in utilization (1.36% to 1.45%) compared to the control group’s significant growth (4.11% to 6.80%), with a difference-in-differences of -2.6%, favoring the diagnosis code group. Cost containment was similarly dramatic, with the diagnosis code group seeing a 15% increase in PMPM costs compared to 79% in the control group. Importantly, this cost containment was achieved while maintaining appropriate access to care, with 78.3% of approved claims processed within one day.
Several factors are critical for successful implementation:
- Clear communication protocols between all stakeholders
- Training and support for pharmacy staff during transition periods
- Established processes for maintaining accurate diagnosis documentation
- Regular monitoring of rejection rates and resolution times
Healthcare systems face increasing pressure to manage costs while maintaining access to innovative but expensive therapies. Automated verification approaches offer a promising path forward. This study demonstrates that technological solutions can effectively balance cost control, appropriate utilization and patient access, while reducing the administrative burden on providers and payers. As medication costs continue to rise and new therapeutic options emerge, effective approaches for benefit management such as this will become increasingly valuable to all healthcare stakeholders.
Disclosure: This research was conducted by Navitus Health Solutions, Madison, WI without external funding. All authors are employees of Navitus Health Solutions.
References
Watanabe JH, Kwon J, Nan B, Reikes A. Trends in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist use, 2014 to 2022. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2024;64(1):133-138. doi: 10.1016/j.japh.2023.10.002.
Han SH, Safeek R, Ockerman K, et al. Public interest in the off-label use of glucagon-like peptide 1 agonist (Ozempic) for cosmetic weight loss: a Google trends analysis. Aesthet Surg J. 2023;44(1):60-67. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjad211.
ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of care in diabetes – 2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(Suppl1):S1-S4. doi: 10.2337/dc23-Sint.
Atlas SJ, Kim K, Nhan E, et al. Medications for obesity management: effectiveness and value. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2023 May;29(5):569-575. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2023.29.5.569.
Leach J, Chodroff M, Qiu Y, et al. Real-world analysis of glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist (GLP-1a) obesity treatment one year cost-effectiveness and therapy adherence. Prime Therapeutics. Published July, 11, 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. www.primetherapeutics.com/documents/d/primetherapeutics/glp-1a-obesity-treatment-1st-year-cost-effectiveness-study-abstract-final-7-11
Stay Informed and Connected
Receive expert insights, healthcare tips, and important updates on pharmacy benefits, drug recalls, and more—straight to your inbox.
Navigating with a trusted partner
Now Available: 9th Annual Drug Trend Report
Our Drug Trend Report provides a clear view of the trends shaping pharmacy benefits today, along with strategies that are delivering real savings without compromising care.